Teamcenter preferences are settings stored in the Teamcenter database that provide a mechanism to control and define Teamcenter behavior by letting you modify the interface, set default behavior, and specify default values.
Use Teamcenter preferences to configure many aspects of a session of application behavior, such as how assemblies are revised, whether extension rules are bypassed for specified operations, and which Teamcenter objects are displayed in integrations. Each application may have associated preferences. They are similar to environment variables, except that they operate with several layers of permissions
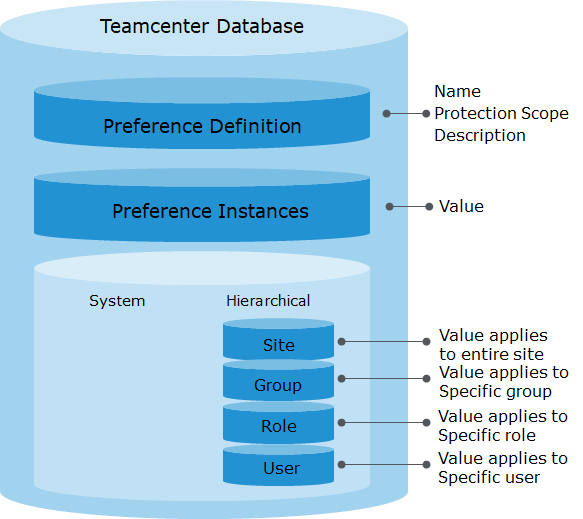
Preference Definition:

 Definition:
Definition:
The preference definition is like a blueprint. It defines the nature of the preference and is used to create the instances at the various locations.
 Site:
Site:
A preference instance created at the site location applies to everyone logged in to Teamcenter unless overridden. There can be only one site instance.
 Group:
Group:
Any preference instances created at the group location apply only to users who are currently logged in as that group, and they supersede site preferences. There can be one group instance created for each group.
 Role:
Role:
Any preference instances created at the role location apply only to users who are currently logged in as that role (regardless of group), and they supersede site and group preferences. There can be one role instance created for each role.
 User:
User:
Any preference instances created at the user location apply only to that user, and they supersede site, group, and role preferences. There can be one user instance created for each user.
Creating Preference Definition:

The name of the preference.
Determines where and by whom it can be instantiated
Organize related preferences based on their category.
Specify the preference value type.
Specify if this preference can hold multiple values.
Explain the use of the preference
Specify the default value that an instance will contain when initially created.
Preference Instance:
Preference instance are created from its definition. Preference instance must belong to a location. Preference instance cannot be created if the protection scope does not allow it.

Preference Location:
User: This assigns the instance to a specific user. Eg: Column widths, most recent search, etc.
Role: Control the behavior based on a user's role. Eg: Stylesheets.
Group: Control the behavior at the next step up, at the group level.
Site/System: Preferences created at these locations apply to everyone.
Site preferences only allow a single instance, but a dba can change the protection scope of a site preference to something else.
System preferences do not allow their protection scope to be changed, even by a dba. In all other ways, they behave like a site preference.
Preference Order of Execution:

If the preference is an Environment preference, tcserver checks the value of the OS environment variable of the same name. If the environment variable exists, the value returned and cached for future requests.
If the preference is not an Environment preference, or if there was no OS value present, tcserver looks for a preference instance at the User location for the current user. If it is found, it returns the value.
If tcserver has not returned a preference value yet, it looks for a preference instance at the Role location for the user's current role. If it is found, it returns the value.
If tcserver has not returned a preference value yet, it looks for a preference instance at the Group location for the user's current group. If it is found, it returns the value.
If tcserver has not returned a preference value yet, it returns the value of the preference instance at the Site / System location.
Who can make changes to preferences:

Any user
Can create, modify, and delete their own User preference instances.
Group Administrator
Can create, modify, and delete the User preference instances of members of their group, as well as Group preference instances for their group and Role instances for any role in their group.
dba
Can create, modify, and delete all preferences at all locations.

Great!
ReplyDelete